Enterprise Cloud Security: Ensuring the Safety of Your Data in the Cloud
What Do You Mean by Enterprise Cloud Security?
Enterprise cloud security refers to the practices, technologies, and policies that are put in place to protect the data, applications, and infrastructure of an organization that are stored in the cloud. With the increasing adoption of cloud services and storage by businesses of all sizes, ensuring the security of this data has become a top priority. The goal of enterprise cloud security is to minimize the risk of data breaches, data loss, and other cyber threats that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information.
How Does Enterprise Cloud Security Work?
Enterprise cloud security involves a combination of tools, techniques, and best practices to protect data in the cloud. This includes encryption to secure data in transit and at rest, access control to limit who can access the data, identity and authentication management to ensure only authorized users can access the data, and monitoring and auditing to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time.
What is Known About Enterprise Cloud Security?
There are a number of key concepts and technologies that are known to be critical for enterprise cloud security. These include:
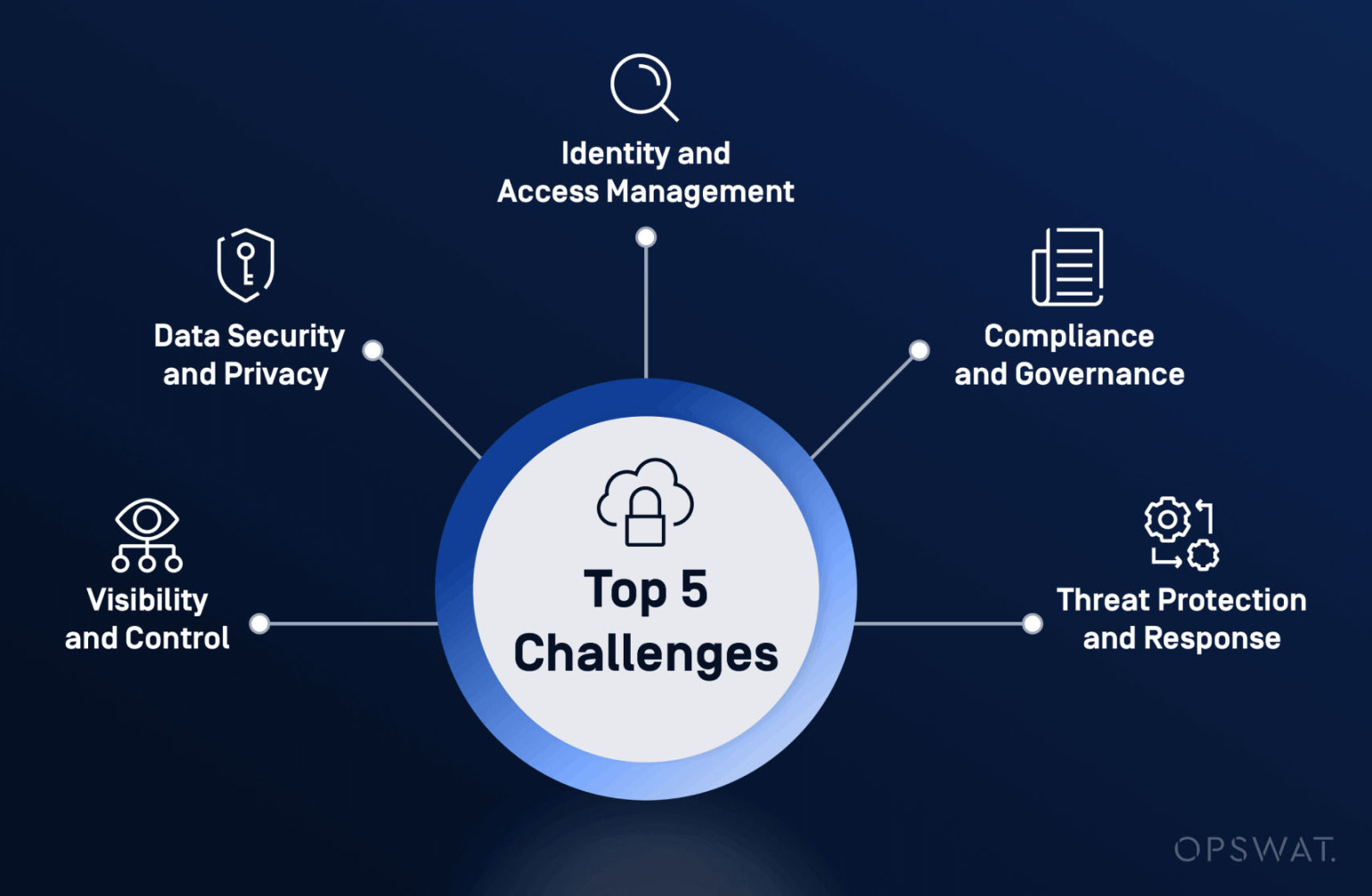
1. Multi-factor authentication: requiring more than one method of authentication to verify the identity of a user
2. Data loss prevention: tools and technologies that prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network
3. Secure access controls: limiting access to data based on the principle of least privilege
4. Security information and event management (SIEM): monitoring and analyzing security events in real-time
5. Secure configuration management: ensuring that cloud services and infrastructure are configured securely
Solution for Enterprise Cloud Security
There are several steps that organizations can take to enhance their enterprise cloud security. These include:
1. Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities
2. Implementing strong encryption protocols to protect data both in transit and at rest
3. Deploying access control mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive data
4. Training employees on best practices for cloud security and the importance of maintaining good security hygiene
5. Regularly monitoring and auditing cloud services and infrastructure for any security incidents
Conclusion
Enterprise cloud security is a critical aspect of modern business operations, as more and more organizations rely on cloud services to store and manage their data. By implementing robust security measures and following best practices, organizations can protect their data from cyber threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information.
FAQs
1. What are the common threats to enterprise cloud security?
Common threats to enterprise cloud security include data breaches, ransomware attacks, insider threats, and misconfigured cloud services.
2. How can I ensure the security of my organization’s data in the cloud?
You can ensure the security of your organization’s data in the cloud by implementing strong encryption, access controls, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
3. What are the benefits of using cloud services for enterprise data storage?
The benefits of using cloud services for enterprise data storage include cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and access to advanced security features.
4. How can I choose the right cloud service provider for my organization?
When choosing a cloud service provider, consider factors such as data security measures, compliance certifications, uptime guarantees, and customer support services.
5. What should I do in case of a security incident in the cloud?
In case of a security incident in the cloud, it is important to have a response plan in place that includes notifying relevant stakeholders, containing the incident, investigating the root cause, and implementing corrective measures to prevent future incidents.



